Do you ever feel like your network infrastructure is a black box? When I first dove into cloud networking, the term Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) sounded mysterious—like a secret compartment in the sky. Over the years, I’ve come to see a VPC as your custom sandbox inside a public cloud: a private playground built on shared real estate.
In this post, we’ll unpack what a VPC really is, how it works under the hood, and why it’s an indispensable tool for any software craftsperson aiming for secure, scalable cloud architecture.
What Exactly is a VPC?
At its core, a VPC is your own slice of a cloud provider’s network fabric. You get to:
- Define your IP address ranges and subnets
- Control traffic flow with route tables and gateways
- Lock things down with security groups and network ACLs
Imagine renting a suite of lockable offices within a massive, secure data center. You share walls, electricity, and internet pipes with other tenants, but your workspace is fully under your control.
Why You Need a VPC
Here’s what a VPC gives you:
- Isolation without the hardware headache — You get private networking without buying switches and routers.
- Security by design — Fine-grained firewalls at both subnet and instance level.
- Elastic scalability — Grow or shrink subnets on demand.
- Hybrid connectivity — Seamless VPN or dedicated link back to your on-prem estate.
Whether you’re hosting a simple website or architecting a multi-region microservices platform, your network perimeter starts here.
Under the Hood: How VPCs Work
Cloud providers stitch together several software-defined networking (SDN) technologies:
- VLAN-style partitioning to segregate traffic flows.
- CIDR-based subnets for logical grouping.
- Virtual routers enforcing your route tables.
- Gateways (Internet or NAT) giving public or controlled outbound access.
VLAN-style partitioning
CIDR-based Subnets
10.0.0.0/16. Within that block, you carve out smaller subnets (e.g., 10.0.1.0/24) by allocating fewer bits to the network prefix. Subnets let you group resources logically, control routing, and apply security rules at a finer granularity.Virtual Routers
Gateways
Gateways connect your VPC to other networks:
- Internet Gateway: Enables resources in a public subnet to send and receive traffic from the internet.
- NAT Gateway: Allows instances in private subnets to initiate outbound internet connections while preventing direct inbound traffic.
- VPN Gateway / Direct Connect: Secures and optimizes connections back to your on-premises network.
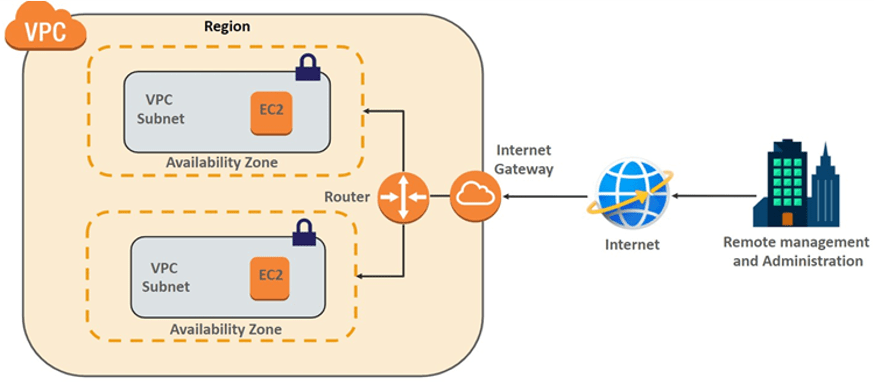
Here’s a simplified diagram of a VPC with public and private subnets:
[Public Internet]
↓
[Internet Gateway]
↓
[Virtual Router]
┌──────────────┐
│ Public │ → [Web Servers]
│ Subnet │
└──────────────┘
↓
┌──────────────┐
│ Private │ → [Databases]
│ Subnet │
└──────────────┘
Subnet Segmentation
Public Subnet
Private Subnet
Security Layers
Security Groups
Network ACLs
Flow Logs
Practical Example: Creating a VPC on AWS
With the AWS CLI, you can spin up a basic VPC in minutes:
# 1. Create a VPC
aws ec2 create-vpc --cidr-block 10.0.0.0/16
# 2. Create subnets
aws ec2 create-subnet --vpc-id vpc-12345 --cidr-block 10.0.1.0/24
aws ec2 create-subnet --vpc-id vpc-12345 --cidr-block 10.0.2.0/24
# 3. Add an Internet Gateway
aws ec2 create-internet-gateway
aws ec2.attach-internet-gateway --vpc-id vpc-12345 --internet-gateway-id igw-67890
# 4. Configure routing
aws ec2.create-route --route-table-id rtb-abcde --destination-cidr-block 0.0.0.0/0 --gateway-id igw-67890
When to Reach for a VPC
- Microservices: Isolate each service tier in its own subnet.
- Hybrid Cloud: Extend on-premise networks for burst capacity.
- Compliance: Enforce strict network controls for regulated workloads.
- Multi-Region: Replicate VPCs in other regions for disaster recovery.
Final Thoughts
A well-designed VPC is the foundation of any solid cloud architecture. It gives you the security posture you need and the flexibility to evolve. Whether you’re a solo craftsperson or part of a large engineering team, mastering VPCs is a step toward cloud craftsmanship.